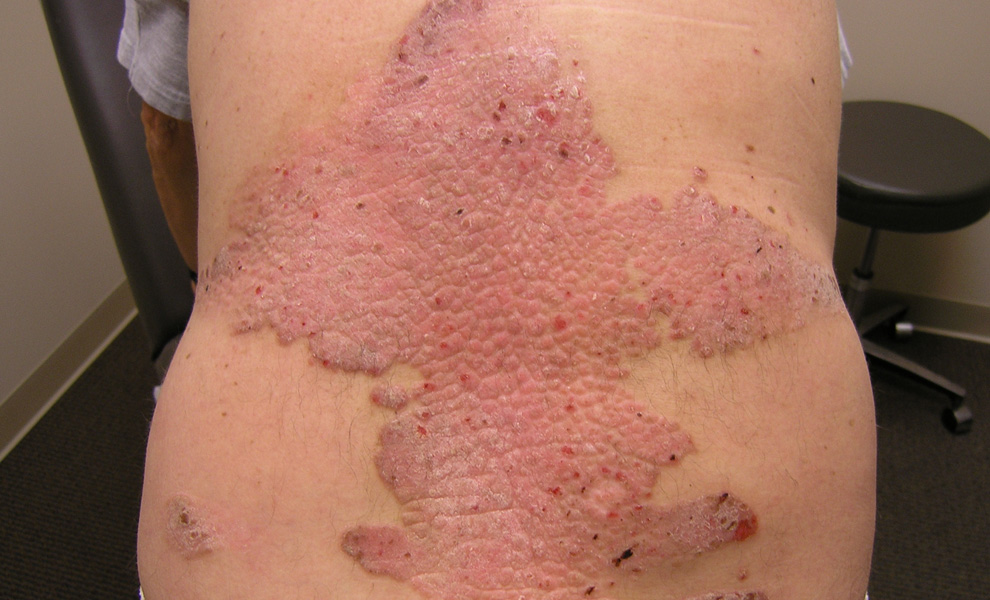
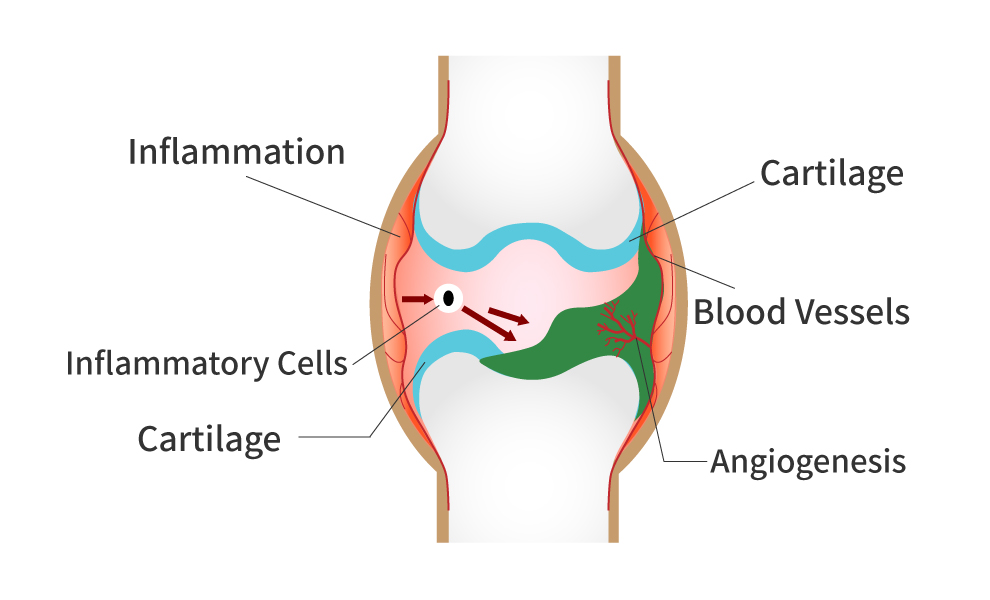
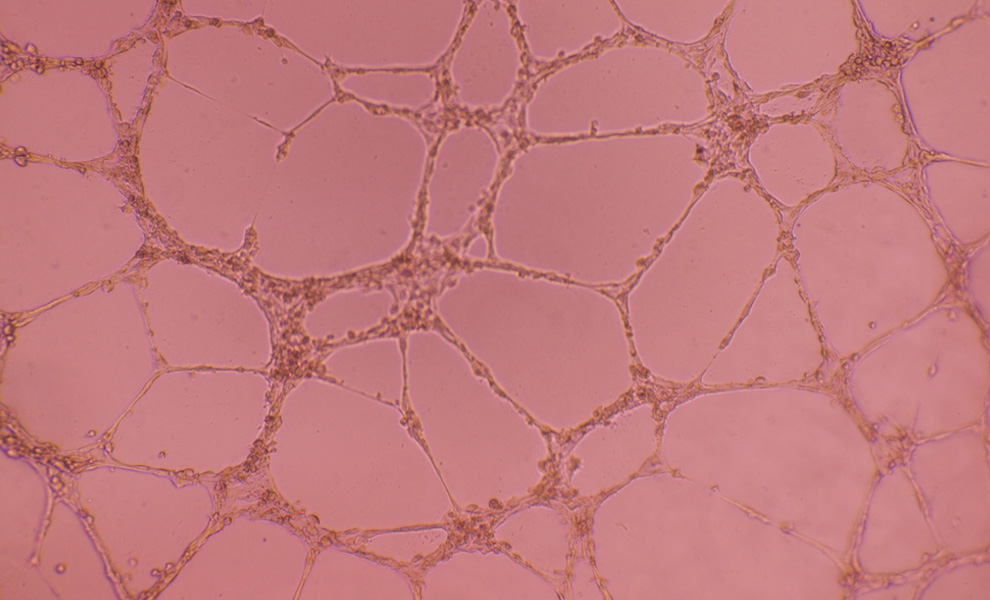
Macolipin is an unique Shark Extracted Lipid. It has strong angiogenesis inhibitory properties which are valuable for inhibiting tumour development and metastasis in cancers. It is also a factor in the pathogenesis and progression of all angiogenesis related disorders including metabolic syndrome, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and age related skin disorders. Angiogenesis means the birth of new blood vessels and, while being an essential function in the normal development and physiology of the body, when related to cancer and other disease states it needs to be inhibited. The following excerpt from an abstract, with added explanatory notes, describes experimental evidence for the effectiveness of Macolipin in inhibiting angiogenesis.
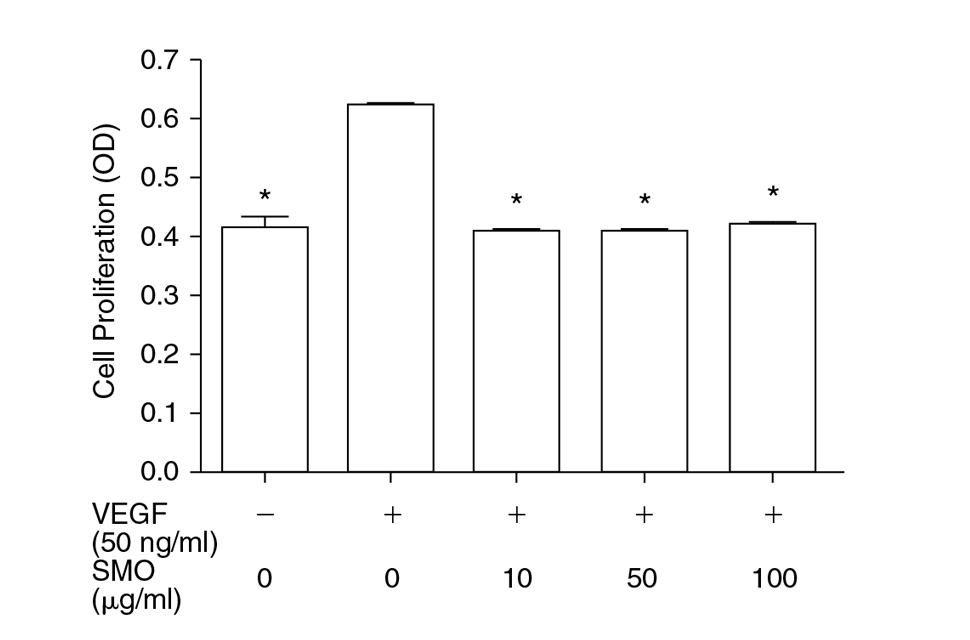
This Shark Extracted Lipid is particularly potent in anti-angiogenesis activity. In laboratory experiments the preparation of Shark Extracted Lipid (Macolipin) which is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (notably docosahexaenoic acid), produced a 50% inhibition of angiogenesis at only 5µg/ml. When administered orally in vivo Macolipin elicited a 50% reduction in angiogenesis at 17mg/kg body weight. Olive oil was shown to have no inhibitory effect in the aortic ring or the in vivo models. However, Macolipin, when combined with olive oil (1:9) was twice as potent in the in vitro system.
The experiments indicate that this combination can negate the stimulatory effects of factors such as VEGF, FGF-2 and TGF-β (These are growth factors that stimulate the connection of tumours to the major blood vessels thus allowing the tumour to grow and to metastasise). They also suggest that Macolipin/Olive oil (1:9) mixture is a potent orally-active natural product that has significant anti-angiogenic effects. The anti-angiogenesis functionality of Macolipin is through the inhibition of binding of VEGF and its receptors (VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-1), and the inhibition of VEGF receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in the VEGF receptor signal transduction pathway. (In simple, very generalised, terms this means that inhibiting the growth factors from attaching to their attachment sites on the blood vessels the next processes needed to allow the signal to start angiogenesis are prevented)
The experimental and in vivo studies conducted on Macolipin, a unique lipid extract derived from the flesh of certain species of shark substances suggest that the product has value as a natural, orally administered anti-angiogenic ingredient. Macolipin has been subjected to safety studies and shown to be non toxic and non teratogenic (free from adverse effects on foetal development in pregnancy) at the Tama Institute, Japan Food Research Laboratories.